WebSphere and Web server high availability
In this section, we discuss WebSphere system availability, including both process and data availability. WebSphere system availability includes WAS and administrative server process availability, as well as data availability. WebSphere availability depends on end-to-end system availability. Any break in the chain can break the whole system and make the WebSphere service unavailable.
WebSphere server process availability is achieved through the WebSphere workload management (WLM) mechanism, while data is made highly available through clustering techniques. The data may include Entity EJB data, servlet session data, and administrative data, including naming and security.
Depending on whether the Web container and EJB container are on the same host and whether vertical and/or horizontal scaling (WLM) is/are used, we can have several configurations with different levels of availability:
Our discussions on the service availability of these configurations assumes that we have HA databases, with session data persisted to an HA database.
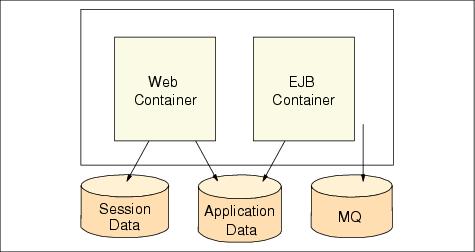
Figure 12-21 Web and EJB container in a single host
When the host dies, the WebSphere service will be unavailable for the configuration shown in Figure 12-21. When either the Web container process or EJB container crashes, the WebSphere service will be unavailable. When the network breaks, the WebSphere service will be unavailable.
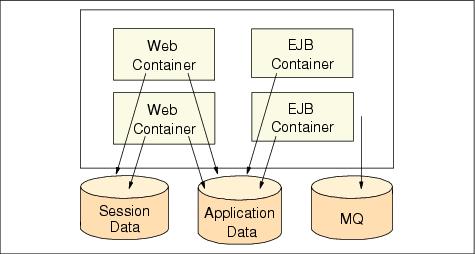
Figure 12-22 Multiple Web and EJB containers in a single host
When the host dies in the configuration shown in Figure 12-22, the WebSphere service will be unavailable. When the network breaks, the WebSphere service will be unavailable. However, when the Web container process and/or the EJB container crashes, the WebSphere service is still available, as long as not all Web containers and EJB containers crash.
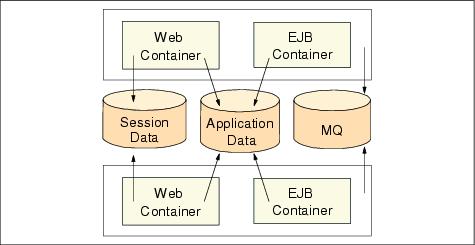
Figure 12-23 Multiple Web and EJB containers in multiple hosts
The configuration shown in Figure 12-23 tolerates both process faults and host faults.
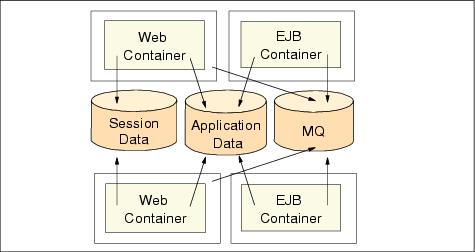
Figure 12-24 Separate Web and EJB containers in multiple hosts
The configuration shown in Figure 12-24 enhances system availability by separating the Web container(s) and EJB container(s). We can also further enhance WebSphere availability by using multiple WebSphere administrative domains so that hardware and software upgrades will not make the system unavailable.
WebSphere is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.
IBM is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.