WebLogic Trap Notifications
You can configure the WebLogic SNMP agent to detect certain thresholds or conditions within a managed resource and send a report (trap notification) to one or more SNMP managers. The WebLogic SNMP agent can generate traps that conform to the SNMPv1 or SNMPv2 protocols.
The following sections describe the trap notifications that the WebLogic SNMP agent can generate:
- Format of WebLogic Trap Notifications
- Automatically Generated WebLogic SNMP Traps
- Log Message Traps
- Monitor Traps
- Attribute Change Traps
For information on configuring or deleting WebLogic Server trap notifications, refer to "Configuring SNMP and WebLogic Server in the Administration Console Online Help.
To see an example of using the weblogic.Admin utility to configure trap notifications, refer to "Using BATCHUPDATE to Configure the WebLogic SNMP Agent in the WebLogic Server Command Reference.
Format of WebLogic Trap Notifications
The WebLogic SNMP agent sends each trap notification to SNMP managers in the form of a protocol data unit (PDU) with the fields indicated in Figure 2-1.

The fields have the following meaning:
- PDU type identifies the packet as a trap notification.
- enterprise is the vendor identification (OID) for the systems/network management subsystem that generated the trap. All traps generated by the WebLogic SNMP agent have the WebLogic OID .1.3.6.1.4.140.625 in the enterprise field.
- agent address is the IP address of the WebLogic Server instance on which the trap was generated.
- generic trap type is an integer in the range of 0 to 6. Table 2-1 lists the values that the different types of WebLogic SNMP traps supply for the generic trap type field.
WebLogic Trap
Generated When
generic trap type Value
coldStart The Administration Server starts. 0 authenticationFailure An SNMP manager sends an incorrect community string. The community string prefix is the actual password and must match the value that you set in the Community Prefix field of the Administration Console. (See SNMP Community Names.) 4 All other WebLogic SNMP traps 6
Traps with a generic trap value of 6 are called enterpriseSpecific traps and are accompanied by a value in the specific trap type field.
- specific trap type is a number that further qualifies an enterpriseSpecific trap. Table 2-2 lists the values that the different types of WebLogic SNMP traps supply for the specific trap type field.
WebLogic Trap
Generated When
specific trap type Value
All Log Message Traps A server instance logs a message that matches user-defined criteria for sending a log notification trap. 60 serverStart Trap A Managed Server that was down is now up. 65 serverShutDown Trap A Managed Server that was up is now down. 70 All Monitor Traps A user-defined JMX monitor detects the crossing of a threshold or occurrence of an event. 75 All Attribute Change Trap An attribute selected by the user has changed in value. 80
- timestamp is the length of time between the last re-initialization of the WebLogic SNMP agent and the time at which the trap was issued.
- variable bindings consists of name/value pairs that further describe the trap notification. Subsequent sections in this topic describe the name/value pairs for each type of trap notification:
Automatically Generated WebLogic SNMP Traps
If you enable the SNMP service for a domain, the WebLogic SNMP agent generates the trap notifications described in Table 2-3. Some of these traps include name/value pairs in the PDU to further describe the event.
|
Trap |
Generated When |
Variable Bindings |
|---|---|---|
| coldStart | The Administration Server starts. | none |
| authenticationFailure | An SNMP manager sends an incorrect community string. The community string prefix is the actual password and must match the value that you set in the Community Prefix field of the Administration Console. (See SNMP Community Names.) | none |
| serverStart | A WebLogic Managed Server that was down is now up. | Contains two name/value pairs to identify server start time and the server name. |
| serverShutDown | A Managed Server that was up is now down. | Contains two name/value pairs to identify server down time and the server name. |
Log Message Traps
Subsystems and deployable modules (such as applications) on a WebLogic Server instance generate log messages to communicate status or other operational data.
Each server instance saves these messages in a local log file and then broadcasts them as JMX notifications. You can set up the WebLogic SNMP agent to listen for all of these messages or you can set up a filter based on criteria such as the following:
- The severity level of the message
- The name of the subsystem that generated the message
- The user ID under which the subsystem is running
- A unique message ID
- A string within the message text
For example, you can specify that only messages from the Security Service of severity level ERROR or higher are sent to the SNMP agent. For information on setting up the SNMP agent to listen for messages, refer to "Create a Notification Log Filter" in the Administration Console Online Help.
When the agent receives a message, it generates an SNMP log notification trap. (See Figure 2-2.)
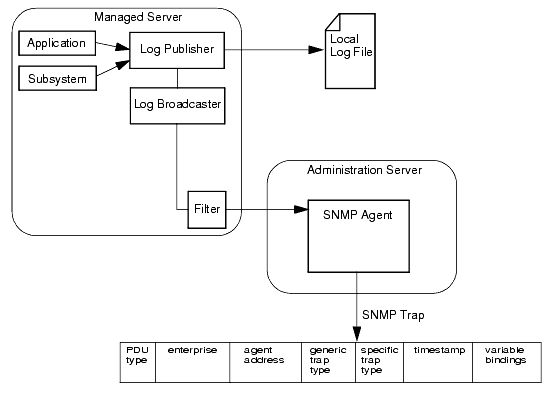
Variable Bindings in Log Message Traps
This section describes the name/value pairs that the log message traps pass to the SNMP manager in the variable bindings field:
- trapTime - Time when the trap is generated.
- trapServerName - Name of the server instance on which the log message was generated.
- trapMachineName - Name of the machine on which the server instance is running.
- trapLogThreadId - Thread ID from the log message.
- trapLogTransactionId - Transaction ID, if any, from the log message. Transaction ID is present only for messages logged within the context of a transaction.
- trapLogUserId - The user ID from the log message. The user ID indicates the security context in which the log message was generated.
- trapLogSubsystem - The subsystem that generated the log message.
- trapLogMsgId - The log message ID from the log message.
- trapLogSeverity - The message severity level from the log message.
- trapLogMessage - The text of the log message.
For more information on log messages and the WebLogic Server logging subsystem, refer to "Server Log in the Administration Console Online Help.
Monitor Traps
To periodically check the value of WebLogic resources for changes, you set up monitors and assign them to instances of WebLogic Server. The monitors poll the MBeans of WebLogic resources at a specified interval and send notifications to the WebLogic SNMP agent when an event that you specify occurs, such as the crossing of a threshold. The SNMP agent generates a trap notification and sends it to the SNMP managers. (See Figure 2-3.)

If you are unfamiliar with WebLogic Server MBeans, refer to "Overview of WebLogic JMX Services in the Programming WebLogic Management Services with JMX guide.
You can configure three types of JMX monitors, depending on the data type of the attribute that you want to observe (the MBean Javadoc describes the type of data that its attributes return):
- Counter Monitor
A counter monitor observes attribute values that are returned as an Integer object type.
You can specify that a trap is generated if an attribute is beyond the bounds of a threshold value. You can also specify that if a value exceeds a threshold, the monitor increases the threshold by an offset value. Each time the observed attribute exceeds the new threshold, the threshold is increased by the offset value, up to a maximum allowable threshold that you specify.
For information on configuring a counter monitor, refer to "Configuring a Counter Monitor in the Administration Console Online Help.
- Gauge Monitor
A gauge monitor observes changes in MBean attributes that are expressed as integers or floating-point.
You can specify that a trap is generated if an attribute is beyond the bounds of a high or low threshold value.
For information on configuring a gauge monitor, refer to "Configuring a Gauge Monitor in the Administration Console Online Help.
- String Monitor
A string monitor observes changes in attributes that are expressed as String objects.
You can specify that a trap is generated if there is a match between the value and the string you provide, or you can specify that the trap is generated if the value differs from the string you provide.
For information on configuring a string monitor, refer to "Configuring a String Monitor in the Administration Console Online Help.
Variable Bindings in Monitor Traps
A JMX monitor polls for a specified threshold or condition and the agent generates a monitor trap when the specified threshold is crossed, or the specified condition occurs. The WebLogic SNMP agent includes the following name/value pairs in the variable bindings of each monitor trap:
- trapTime - The time at which the trap was generated.
- trapServerName - The local server whose attribute value generated the trap.
- trapMonitorType - Either CounterMonitor, StringMonitor, or GaugeMonitor.
- trapMonitorThreshold - An ASCII representation of the threshold that triggered the trap.
- trapMonitorValue - An ASCII representation of the value that triggered the trap.
- trapMBeanName - The name of the MBean that contained the attribute being monitored.
- trapMBeanType - The type of the MBean that contained the attribute being monitored.
- trapAttributeName - The name of the attribute whose value triggered the trap.
Attribute Change Traps
While you can use JMX monitors to periodically poll WebLogic Server resources for changes to attributes that exceed the bounds of specific thresholds, you can also configure the SNMP agent to send a trap immediately after an attribute is changed in any way. For example, you can use a monitor to poll for changes in the current number of active JDBC pools. If the number of active pools exceeds a threshold, the SNMP agent can send a trap. You would use an attribute change trap to detect whether an attribute such as the name of a JDBC pool or the listen port has been changed.
For information on configuring the SNMP agent to send attribute change traps, refer to "Configuring an Attribute Change in the Administration Console Online Help.
Variable Bindings in Attribute Change Traps
An attribute change trap notification includes the following name/value pairs in the variable bindings:
- trapTime - The time at which the trap was generated.
- trapServerName - The name of the Administration Server.
- trapMBeanName - Name of the MBean that includes the attribute.
- trapMBeanType - Type of the MBean that includes the attribute.
- trapAttributeName - Name of the configuration attribute that has changed.
- trapAttributeChangeType - The value can be either ADD, REMOVE, or UPDATE.
- trapAttriruteOldVal - Value of the attribute before the change.
- trapAttributeNewVal - Value of the attribute after the change.
Note: Creation of monitors for changes in run-time attributes is not supported. Only attributes in the configuration MIB can be monitored for change of attribute value.
|
|
|