Variables and imported Java classes
HATS variables
In HATS, there are two main types of variables; global variables and macro variables. The differences between them are outlined here.
Global variables
Global variables are variables created in HATS Studio and used by HATS projects. Global variables are stored outside of the macro script in the HATS .hma source file. They are maintained and updated by HATS runtime. There are two types of global variables:
- Local
- A local global variable is one that is created within a HATS project, and is only visible to the project.
- Shared
- A shared global variable is one that is visible to and can be used by all the applications in an .ear file.
Whether a global variable is considered local or shared depends on whether the shared check box in the GUI is checked when the global variable is created, or whether the value of the shared attribute of a set, prompt, or extract tag is specified as yes or no in the HATS .hma source file.
Macro variables
Macro variables are variables created in the Advanced Macro Editor. Macro variables are internal to macros. They are not used outside of macros. Macro variables are created, stored, and used by the macro engine, and listed in the macro script.
In the source of a HATS macro (.hma) file that uses HATS prompts and extracts for global variables, the prompts and extracts are contained in the source file before the macro script. The macro script syntax is enclosed by the <HAScript> and </HAScript> tags.
Introduction to macro variables and imported types
Macro variables help you to add programming intelligence to macros. With a variable you can store a value, save a result, keep a count, save a text string, remember an outcome, or do any number of other programming essentials.
You can create a variable that belongs to any of the standard data types (string, integer, double, boolean, and field).
You can also create a variable that belongs to an imported type representing a Java class. You can then create an instance of the class and call a method on the instance. This capability opens the door to the abundant variety of functionality available through Java class libraries, including libraries in the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) libraries, classes or libraries that you implement yourself, or Java classes and libraries from other sources.
Advanced macro format required
Using variables requires that you use the advanced macro format for your macro (see Basic and advanced macro format). Therefore, if you want to add variables to a macro that is in the basic macro format, decide whether to convert the macro to the advanced macro format. If you have an old macro in the basic macro format that many users rely on and that works perfectly, you might want to leave the macro as it is.
However, remember that all recorded macros are recorded in the basic macro format. So, if you have recently recorded a macro and are beginning to develop it further, then you might simply not have gotten around to switching to the advanced macro format.
The Macro Editor addresses both these situations by popping up a window with the following message when you start to define a variable in a macro that is still in the basic macro format:
You are attempting to use an advanced macro feature. If you choose to continue, your macro will automatically be converted to advanced macro format. Would you like to continue?
Click Yes if you are building a macro in which you plan to use variables, or No if you have a macro in the basic macro format that you do not want to convert.
Scope of variables
The scope of every variable is global with respect to the macro in which the variable is created. That is, every variable in a macro is accessible from any macro screen in the macro. All that an action or a descriptor in a macro screen has to do to access the variable is just to use the variable name.
For example, suppose that you have a variable named $intPartsComplete$ that you initialize to 0. You might use the variable in the following ways as the macro proceeds:
- ScreenC completes Part 1 of a task and increments $intPartsComplete$ using a Variable update action.
- ScreenG completes Part 2 of a task and increments $intPartsComplete$ using a Variable update action.
- ScreenM has a Conditional action that tests whether 1 or 2 parts have been completed so far. Depending on the result, the macro expects either ScreenR or ScreenS as the next macro screen to be processed.
- ScreenS completes Part 3 of a task and increments $intPartsComplete$ using a Variable update action.
In the example above, actions in several different macro screens were able to read from or write to the variable $intPartsComplete$.
Introduction to the Variables tab
Because a variable belongs to the entire macro, and not to any one screen, it seems appropriate that there is a separate high-level tab for Variables. The Variables tab allows you to:
- Create a variable
- Remove a variable
- Import a Java class as a new variable type
To create a variable belonging to a standard data type, use the Variables tab in the Macro Editor. Figure 43 shows a sample Variables tab:
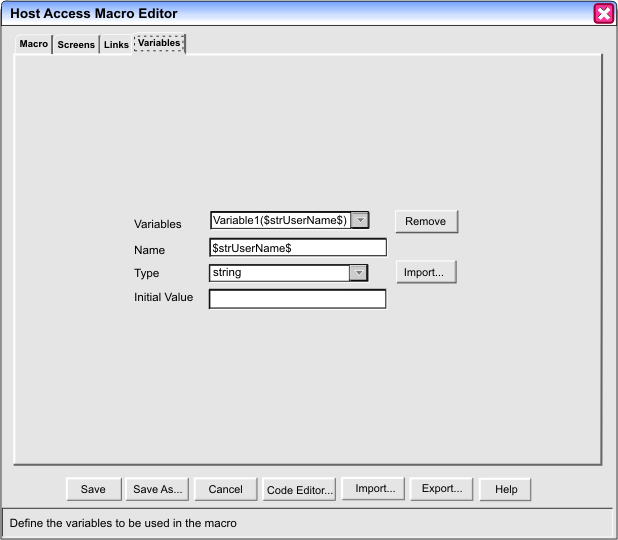
In the figure above, the Variables tab of the Macro Editor is selected. The name of the currently selected variable, $strUserName$, is displayed in the Variables listbox. Three other fields contain information that the macro runtime needs to create this variable: the Name input field, the Type listbox, and the Initial Value input field.
The Variables listbox contains the names of all the variables that have been created for this macro. It allows you to select a variable to edit or to remove, and it also contains a <new variable> entry for creating new variables.
Notice that the entry of the currently selected variable is contained in parentheses after another string:
Variable1($strUserName$)
The string Variable1 is a setting that shows how many variables you have created. It is not saved in the macro script. The real name of the variable is $strUserName$, and you should use this name alone throughout the macro wherever you use the variable.
You have probably noticed that the variable name $strUserName$ is enclosed in dollar signs ($). This is a requirement. You must enclose the variable name in dollar signs ($) wherever you use it in the macro.
The Name input field displays the name of the currently selected variable, $strUserName$. You can change the name of the variable by typing over the old name. Mostly you should use this field only for assigning a name to a newly created variable. Although you can come back later at any time and change the name of this variable (for example to $strUserFirstName$), remember that you might have already used the variable's old name elsewhere in the macro, in some action or descriptor. If you change the name here in the Variables tab, then also go back to every place in the macro where you have you used the variable and change the old variable name to the new variable name.
You can choose any variable name you like, although there are a few restrictions on the characters you can choose (see Variable names and type names). You do not have to choose names that begin with an abbreviated form of the data type (such as the str in the string variable $strUserName$), as this book does.
The Type listbox lists the available types for variables and lets you select the type that you want to use for a new variable. The standard types are string, integer, double, boolean, and field. Also, whenever you import a Java class, such as java.util.Hashtable, as an imported type, the Type listbox picks up this imported type and adds it to the list of available types, as shown in Figure 44:
string integer double boolean field java.util.Hashtable
You should use this listbox for assigning a type to a newly created variable. You can come back later and change the variable's type to another type, but, as with variable names, remember that you might have already used the variable throughout the macro in contexts that require the type that you initially selected. If so, go to each of those places and make sure that the context in which you are using the variable is appropriate for its new type.
The Initial Value input field allows you to specify an initial value for the variable. The Macro Editor provides the following default values, depending on the type:
| Type of variable: | Default initial value: |
|---|---|
| string | No string |
| integer | 0 |
| double | 0.0 |
| boolean | false |
| field | (No initial value) |
| (any imported type) | null |
To specify a new initial value just type over the default value.
The Remove button removes the currently selected variable.
The Import button and the Import popup window are discussed in Creating an imported type for a Java class.
Creating a new variable
To create a new variable in the Macro Editor, first click the <new variable> entry at the end of the Variable listbox. The Macro Editor creates a new variable and assigns to it some initial characteristics that you should modify to fit your needs. The initial values are:
- An initial name (such as $a1$).
- An initial type (string).
- An initial value, which depends on the type (see Table 16).
Now you should set the values that you want for the new variable. For example, if you are creating an integer variable that is for counting screens and that should have an initial value of 1, then you might set the initial values as follows:
- In the Name input field, type the name $intScreenCount$.
- In the Type listbox, select the integer data type.
- In the Initial Value field, type 1.
Besides the Variables tab, the Macro Editor provides access, in several convenient locations, to a popup window for creating new variables. For example, in the Variable update action, the Name listbox contains not only all the names of variables that you have already created but also a <New Variable> entry. Click this entry to bring up the popup window for creating a new variable. Variables created using this popup window are equivalent to variables created in the Variables tab.
In the source view, you create a new variable using a <create> element. There is a containing element called <vars> that contains all the variables in the macro script, and there is a <create> element for each variable. Figure 45 shows a <vars> element that contains five <create> elements:
<vars> <create name="$strAccountName$" type="string" value="" /> <create name="$intAmount$" type="integer" value="0" /> <create name="$dblDistance$" type="double" value="0.0" /> <create name="$boolSignedUp$" type="boolean" value="false" /> <create name="$fldFunction$" type="field" /> </vars>
In the figure above the <vars> element creates one variable from each of the standard data types (string, integer, double, boolean, and field). You should notice that the attributes of each <create> element match the fields on the Variables tab: the name attribute contains the variable name, the type attribute contains the type, and the value field contains the initial value.
You must put all variable creations (<create> elements) inside the <vars> element. The <vars> element itself must appear after the <import> element, if any (see the next section), and before the first macro screen (<screen> element).
Creating an imported type for a Java class
The way that a Host On-Demand macro imports a Java class is through an imported type. That is, first create an imported type and associate it with a particular Java class. You have to do this only once per Java class per macro. Follow these steps to create an imported type:
- On the Variables tab, click the Import button. The Import popup window appears.
- In the Imported Types listbox, select the entry <new imported type>.
- Type the Class name for the type, such as java.util.Hashtable. You must type the fully qualified class name, including the package name if any.
- Type a Short Name, such as Hashtable. If you do not specify a short name then the Macro Editor uses the fully qualified class name as the short name. If you do specify a short name then you can use either the short name or the fully qualified class name when you refer to the imported type.
- Click OK.
To create a variable belonging to this imported type, create the variable in the normal way, but select the imported type as the type of the variable. Follow these steps to create a variable of the imported type:
- In the Variables listbox, click the <new variable> entry at the end. The Macro Editor displays the default initial values in the usual way, including a name (such as $a1$), a type (string), and an initial value (blank).
- In the Name input field, type the name that you want, such as $ht$.
- In the Type listbox, select the imported type, such as Hashtable (if you specified a short name when you imported the type) or java.util.Hashtable (if you accepted the default short name, which is the same as the fully qualified class name).
- In the Initial Value field, you can either leave the field blank (which results in an initial value of null) or specify a method that returns an instance of the class, such as $new Hashtable()$ (using the short name) or $new java.util.Hashtable()$ (using the fully qualified class name).
Notice that the constructors are enclosed in dollar signs ($). You must use dollar signs around every call to a Java method, just as use dollar signs around the name of a variable. (The reason is that the enclosing dollar signs tell the macro runtime that it needs to evaluate the item.)
Going back to the Import popup window, the Imported Types listbox allows you to create new types and to edit or delete the types that you have already created. To create a new type, click the <new imported type> entry at the end of the list. To edit a type, select the type in the Imported Types listbox and modify the values in the Class and Short Name input fields. To remove a type, select the type and click Remove.
When you specify a short name, you can use any name, with certain restrictions (see Variable names and type names).
In the source view, you create an imported type using a <type> element. There is a containing element called <import> that contains all the imported types in the macro script, and there is a <type> element for each imported type. Figure 46 shows an <import> element that declares an imported type, followed by a <vars> element that creates and initializes a variable belonging to the imported type:
<import> <type class="java.util.Hashtable" name="Hashtable" /> </import> <vars> <create name=$ht$ type="Hashtable" value="$new Hashtable(40)$" /> </vars>
In the figure above the <import> element contains one <type> element, which has a class attribute (containing the fully qualified class name, java.util.Hashtable) and a name attribute (containing the short name, Hashtable). The <vars> element contains one <create> element, which as usual specifies a name ($ht$), a type (Hashtable), and an initial value (which here is not null but rather is a call to a constructor that returns an instance of the class, $new Hashtable(40)$).
If you are using the source view, put all imported types (<type> elements) inside the <import> element. The <import> element itself must appear inside the <HAScript> element (see <HAScript> element) and before the <vars> element.
Issues you should be aware of
Deploying Java libraries or classes
During macro playback, when the macro runtime processes a call to a Java method, the macro runtime searches all the available Java library files and class files for the class to which the method belongs, until it finds the class.
Deploying a Java library or class consists of placing the library file or class file containing the class in a location where the macro runtime can find it during macro playback.
- Classes in the Java API (the Java archive files are already present in the HATS application and their locations are listed in the classpath that is specified when the HATS application is launched).
- Classes in the Host On-Demand Macro Utility Libraries (HML libraries) are stored with the HATS code (see The Macro Utility Libraries (HML libraries)).
All other Java classes containing methods invoked by a macro script must be deployed by you to a location where the macro runtime can find them. Depending on the environment, you can deploy the Java classes as class files or as libraries containing Java classes.
Variable names and type names
The rules for variable names are as follows:
- A variable name can contain only alphanumeric characters (a-z, A-Z, 0-9), underscore (_), or hyphen (-).
- Case is significant (for example, strTmp and strtmp are two different names).
- A variable name cannot be the same as the short name or the fully qualified class name of an imported type.
The rules for type names are as follows:
- A type name can contain only the alphanumeric characters, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or period (.).
- Case is significant.
Transferring variables from one macro to another
The PlayMacro action, in which one macro "chains to" another macro (a call without return), allows you to transfer all the variables and their values belonging to the calling macro to the target macro. The target macro has access both to its own variables and to the transferred variables (see PlayMacro action (<playmacro> element)).
Field variables
A field variable is a type of string variable. It holds a string, just as a string variable does, and you can use it in any context in which a string variable is valid.
However, a field variable differs from a string variable in the way in which a string is stored into the field variable. The string that a field variable contains is always a string that the macro runtime reads from a 3270 or 5250 field in the current host terminal. To get the macro runtime to read this string from the 3270 or 5250 field, you have to create a Variable update action that specifies:
- The name of the field variable (such as $fldFilename$).
- A location string (a string containing a pair of integers separated by a comma, such as '5,11').
When the macro runtime performs the Variable update action it takes the following steps:
- Looks in the host terminal at the row and column value specified by the location string.
- Finds the 3270 or 5250 field in which the row and column value is located.
- Reads the entire contents of the field.
- Stores the entire contents of the field as a string into the field variable.
For more information, see Variable update action with a field variable.
Using variables
When variables are initialized
The macro runtime assigns initial values to variables at the start of the macro playback, before processing any macro screen.
Using variables belonging to a standard type
Using the value that the variable holds
A variable that belongs to a standard type (string, integer, double, boolean) can be used in much the same way as an immediate value of the same type (such as 'Elm Street', 10, 4.6e-2, true):
- Except for the restrictions listed later in this subsection, a variable of standard type can be used in any input field (in the Macro Editor) or attribute (in the source view) in which an immediate value of the same data type can be used. For example, if an input field requires a string value, then the field likewise accepts a string variable. See Equivalents.
- Variables can be used with operators and expressions in the same ways that immediate values of the same types are used. See Operators and expressions.
- The value of a variable occurring in a context different from the type of the variable is converted, if possible, to a value of the correct type, in the same way that an immediate value of the same type is converted. See Automatic data type conversion.
However, you cannot use a variable in certain contexts. In the Macro Editor, you cannot use a variable in the following contexts:
- Any field on the General tab.
- The Screen Name field on the Screens tab.
- The value of any field in the PlayMacro action window.
In the source view, you cannot use a variable in the following contexts:
- The name of an attribute of any element.
- The value of any attribute of an <HAScript> element.
- The value of the name attribute of a <screen> element.
- The value of the uselogic attribute of the <description> element.
- The name of a macro screen in a <nextscreen> element.
- The value of any attribute of a <playmacro> element.
Writing a value into a variable belonging to a standard type
You can write a value into a variable belonging to a standard type in the following ways:
- Assign an initial value when you create the variable.
- Use a Variable update action to assign a value to the variable.
- Use the Prompt action to get user input and assign it to the variable.
- Use the Extract action to read data from the host terminal and assign it to the variable.
- Use an action that writes a return code value into a variable.
Restrictions
You cannot assign one of the following values to a variable of standard type:
- The value null. (Exception: If you assign the value null to a string variable, it is converted to the string 'null').
- A call to a void method.
- A call to a method that returns an array.
Writing a Java object into a variable of standard type
If you write a Java object into a variable of standard type, then the macro runtime calls the toString() method of the imported type and then attempts to assign the resulting string to the variable.
Using variables belonging to an imported type
Using the value that the variable holds
You can use the value contained in a variable belonging to an imported type in the following ways:
- You can assign the variable to another variable of the same type using the Variable update action.
- You can call a Java method on the variable (see Calling Java methods). If the Java method returns a value belonging to a standard type (string, integer, double, boolean), then you can use the result as you would use any value of that type.
Restrictions
You cannot assign the following types of data to a variable of imported type:
- A value or variable belonging to a standard type (string, integer, double, boolean, field).
- A instance of, or a variable belonging to, a different imported type (unless it is a superclass of the imported type).
- An array of instances of objects returned by a method called on a variable of imported type.
If your macro attempts to assign one of these invalid types of values to a variable of imported type, then the Macro runtime generates a runtime error and halts the macro
Writing into the variable belonging to an imported type
You can write a value into a variable of imported type in the following ways:
- You can assign a value to the variable when you create it.
- You can assign a value to the variable using the Variable update action.
You can assign the following types of values to a variable belonging to an imported type:
- An instance of the same type. This instance can be either in a variable of the same type, or from a call to a method that returns an instance of the same type.
- The value null. To signify the value null, you can use one of the following:
- The keyword null.
- A blank input field (if you are using the Macro Editor), such as the Initial Value field on the Variables tab, or the Value field on the Variable update window.
- An empty attribute (if you are using the source view), as in the value attribute of the following <create> element:
<create name=$ht$ type="Hashtable" value="" />
Comparing variables of the same imported type
In any conditional expression (for example, in the Condition field of a conditional action) in which you are comparing two variables of the same imported type, you should implement a comparison method (such as equals()) in the underlying class rather than using the variables themselves. For example,
$htUserData.equals($htPortData$)$
If instead, you compare the variables themselves (for example $htUserData$ == $htPortData$), then:
- The macro runtime, for each variable, calls the toString() method of the underlying Java class and gets a string result
- The macro runtime compares the two string results and gets a boolean result.
- The macro runtime sets the result of the condition to the boolean result obtained in step 2.
This will probably not yield the outcome that you expect from comparing the two variables.
Calling Java methods
Where method calls can be used
You can call a method in any context in which the value returned by the method is valid. For example, in an Input action you can set the Row value to the integer value returned by a method, such as:
$importedVar.calculateRow()$
Also, you can use the Perform action to call a method when you do not need the return variable of the method or when the method has no return value (void) (see Perform action (<perform> element)).
Syntax of a method call
To call a method belonging to an imported class, use the same syntax that you would use in Java. However, in addition, also enclose a method call in dollar signs ($), just as you would a variable. Examples:
$new FileInputStream('filename')$
$fis.read()$ An immediate string value (such as 'Elm Street', or 'myFileName' in the first example above) passed as a parameter to a method must be enclosed in single quotes, as usual (see In the advanced macro format, rules for representation of strings, etc.).
How the macro runtime searches for a called method
When you add a method call (such as $prp.get('Group Name')$) to a macro script, the Macro Editor does not verify that a called method or constructor exists in the class to which the variable belongs. That check is done by the macro runtime when the call occurs.
The method must be a public method of the underlying Java class.
When the macro runtime searches in the Java class for a method to match the method that you have called, the macro runtime maps macro data types (boolean, integer, string, field, double, imported type) to Java data types as shown in Table 17:
| If the method parameter belongs to this macro data type: | Then the macro runtime looks for a Java method with a parameter of this Java data type: |
|---|---|
| boolean | boolean |
| integer | int |
| string | String |
| field | String |
| double | double |
| imported type | underlying class of the imported type |
The macro runtime searches for a called method as follows:
- The macro runtime searches for the class specified in the imported type definition (such as java.util.Properties).
- The macro runtime searches in the class for a method with the same method signature (name, number of parameters, and types of parameters) as the called method.
- If the search succeeds, then the macro runtime calls the method.
- If the search fails, then the macro runtime searches in the class for
a method with the same name and number of parameters (disregarding the types
of the parameters) as the called method.
- If the macro runtime finds such a method, it calls the method with the specified parameters.
- If the call returns without an error, the macro runtime assumes that it has called the right method.
- If the call returns with an error, the macro runtime searches for another method.
- The search continues until all methods with the same name and number of parameters have been tried. If none was successful, then the macro runtime generates a runtime error.
The Macro Utility Libraries (HML libraries)
The Host On-Demand Macro Utility Libraries (HML libraries) are utility libraries that are packaged with the HATS code. You can invoke a method from one of these libraries without:
- Importing the underlying class; or
- Creating a variable to contain an instance of the class; or
- Creating an instance of the class.
In fact, you are not allowed to import a class contained in an HML Java library, or to create a variable belonging to an HML class, or to create an instance of an HML object.
The reason is that the macro runtime, during the initializing that goes on when macro playback is started:
- Imports all the HML classes.
- Creates one variable for each HML class to contain an instance of the class.
- Creates one instance of each HML class and stores it in the appropriate variable.
The following table shows for each HML variable the variable name and the types of methods in the underlying class.
| HML variable: | Description of methods: |
|---|---|
| $HMLFormatUtil$ | Methods for formatting strings. |
| $HMLPSUtil$ | Methods that access the presentation space of the session window. |
| $HMLSessionUtil$ | Methods that return session values. |
| $HMLSQLUtil$ | Methods that return information about the results of the most recent SQLQuery action. |
Invoking an method belonging to an HML library
To invoke a method belonging to an HML library, specify the variable name, method name, and input parameters in the usual way:
$HMLFormatUtil.numberToString(1.44)$ $HMLPSUtil.getCursorPos()$ $HMLSessionUtil.getHost()$
Variables names beginning with HML are reserved
To prevent confusion between normal variables and HML variables, variable names beginning with HML are reserved. If you try to create a variable beginning with HML, Host On-Demand generates an error message.
$HMLFormatUtil$
The methods invoked with $HMLFormatUtil$ are formatting methods. Table 19 summarizes these methods:
| METHOD SUMMARY: $HMLFormatUtil$ | |
|---|---|
| String |
|
| int or double |
|
Converting numbers to and from the format of the current locale
A locale is a set of formatting conventions associated with a particular national language and geographic area. For example, depending on the locale with which a client workstation is configured, a decimal value such as 1111.22 can be represented with any of the following strings:
'1111.22' '1,111.22' '1111,22'
As another example, a negative number such as -78 can be represented as:
'-78' '78-'
The methods numberToString() and stringToNumber() perform conversions between a number (that is, a variable or immediate value of type integer or type double, such as 1111.22) and its representation in the current locale (a string, such as '1111.22', '1,111.22', or '1111,22').
Method details
numberToString()
public String numberToString(Object obj)
This method converts a number (integer or double) to a string formatted according to the currently configured locale. The input parameter can be of type integer or of type double.
This method replaces the standalone method $FormatNumberToString()$, which is deprecated.
<input value="$HMLFormatUtil.numberToString(1111.44)$"
row="20" col="16" movecursor="true"
xlatehostkeys="true" encrypted="false" />
stringToNumber()
public int stringToNumber(String str) public double stringToNumber(String str)
This method converts a numeric string formatted according to the currently configured locale to a number. The number returned is either of type integer or of type double, depending on the input string.
This method replaces the standalone method $FormatStringToNumber()$, which is deprecated.
<message title="'stringToNumber()'" value="'1111.33'" />
<extract name="'Extract'" planetype="TEXT_PLANE"
srow="1" scol="1"
erow="1" ecol="10" unwrap="false"
assigntovar="$value$" />
<if condition="$HMLFormatUtil.stringToNumber($value$)$ < 0 "
...
</if>
$HMLPSUtil$
The methods invoked with $HMLPSUtil$ affect the presentation space of the session window or return information about the presentation space of the session window. Table 20 summarizes these methods:
| METHOD SUMMARY: $HMLPSUtil$ | |
|---|---|
| int |
|
| int |
|
| void |
|
| int |
|
| int |
|
| int |
|
| int |
|
| int |
|
| int |
|
| String |
|
| int |
|
Presentation space
The presentation space is a data structure that contains an element for each row and column position in the session window (but not including the last row of the session window, which is used for the Operator Information Area). The size of the presentation space depends on the size of the session window. For example, if the session window has 80 rows and 25 columns, then the size of the presentation space is 80 * 24 = 1920.
The position of the elements in the presentation space corresponds serially to the row and column positions in the session window, reading from left to right, top to bottom. For example, if the session window has 80 rows and 25 columns, then:
Row of Column of Corresponds to
Session Session element at this
Window: Window: position in PS:
1 1 1
1 2 2
1 3 3
...
1 80 80
2 1 81
2 2 82
2 3 83
...
24 79 1919
24 80 1920
Host On-Demand uses the presentation space to store the characters that are to be displayed in the session window. Each element in the presentation space is used to store one character (and information about that character, such as intensity). For example, if the string Message appears at row 1 and column 1 of the session window, then:
Row of Column of Corresponds Character
Session Session to element stored in
Window: Window: at this pos- this element:
ition in PS:
1 1 1 M
1 2 2 e
1 3 3 s
1 4 4 s
1 5 5 a
1 6 6 g
1 7 7 e
Although you normally will not need to use them, Table 21 show the formulas for calculating various values. The meanings of the symbols used in these formulas is as follows:
- row - A row location in the session window
- col - A column location in the session window
- pos - A position in the presentation space
- NUMROWS - The number of rows in the session window, not including the last row used for the Operator Information Area (OIA).
- NUMCOLS - The number of columns in the session window.
| Value: | Formula for calculating: |
|---|---|
| Size of the PS |
NUMROWS * NUMCOLS
Example:
24 * 80 = 1920
|
| row |
(pos + NUMCOLS - 1) / NUMCOLS
Example:
(81 + 80 - 1) / 80 = 2
|
| col |
pos - ((row - 1) * NUMCOLS)
Example:
1920 - ((24 - 1) * 80) = 80
|
| pos |
((row - 1) * NUMCOLS) + col
Example:
((24 - 1) * 80) + 1 = 1641
|
Method details
convertPosToCol()
public int convertPosToCol(int pos)
This method returns the column number associated with the specified position in the presentation space.
<message title="'Example of convertPosToCol()'"
value="'Cursor is at column '+
$HMLPSUtil.convertPosToCol($HMLPSUtil.getCursorPos()$)$" />
convertPosToRow()
public int convertPosToRow(int pos)
This method returns the row number associated with the specified position in the presentation space.
<message title="'Example of convertPosToRow()'"
value="'Cursor is at row '+
$HMLPSUtil.convertPosToRow($HMLPSUtil.getCursorPos()$)$" />
enableRoundTrip()
public void enableRoundTrip(boolean flag)
This method is for bidirectional languages only (Arabic and Hebrew). Assume that A, B, and C are bidirectional characters. Normally, when a string contains a series of bidirectional characters followed by a series of numerals (for example, ABC 123), and the entire string is stored, the Host On-Demand client exchanges the positions of the bidirectional characters and the numerals. For example, normally, if you read the string ABC 123 from the presentation space and store the string into a variable, and then subsequently write the value of the variable back into the presentation space, the Host On-Demand client writes 123 ABC back into the presentation space.
To turn off this technique of forced reversal, call enableRoundTrip() with a value of true. To restore this technique of forced reversal, call enableRoundTrip() with a value of false.
<perform value="$HMLPSUtil.enableRoundTrip(true)$" />
getCursorCol()
public int getCursorCol()
This method returns the column location of the text cursor in the presentation space.
<input value="$HMLSessionUtil.getHost()$"
row="$HMLPSUtil.getCursorRow()$"
col="$HMLPSUtil.getCursorCol()$+2"
movecursor="true" xlatehostkeys="true"
encrypted="false" />
getCursorPos()
public int getCursorPos()
This method returns the position of the text cursor in the presentation space.
<message title="'Example of getCursorPos()'"
value="'Cursor is at row '+
$HMLPSUtil.convertPosToRow($HMLPSUtil.getCursorPos()$)$+
' and column '+
$HMLPSUtil.convertPosToCol($HMLPSUtil.getCursorPos()$)$" />
getCursorRow()
public int getCursorRow()
This method returns the row location of the text cursor in the presentation space.
<input value="$HMLSessionUtil.getHost()$"
row="$HMLPSUtil.getCursorRow()$"
col="$HMLPSUtil.getCursorCol()$+2"
movecursor="true" xlatehostkeys="true"
encrypted="false" />
getSize()
public int getSize()
This method returns the size of the presentation space, that is, the number of character positions in the presentation space. For example, if the session window has 25 rows and 80 columns, then the size of the presentation space is 24 * 80 = 1920.
<message title="'Example of getSize()'"
value="'Size of PS is '+$HMLPSUtil.getSize()$" />
getSizeCols()
public int getSizeCols()
This method returns the number of columns in the presentation space. The presentation space has the same number of columns as the session window. For example, if the session window has 25 rows and 80 columns, then the number of columns in the presentation space is 80.
<message title="'Example of getSizeRows and getSizeCols()'"
value="'The PS has '+$HMLPSUtil.getSizeRows()$+
' rows and '+
$HMLPSUtil.getSizeCols()$+' columns'" />
getSizeRows()
public int getSizeRows()
This method returns the number of rows in the presentation space. The presentation space has one row less than the session window (because the last line of the session window, which contains the Operator Information Area, is not included in the presentation space). For example, if the session window has 25 rows and 80 columns, then the number of rows in the presentation space is 24.
<message title="'Example of getSizeRows and getSizeCols()'"
value="'The PS has '+$HMLPSUtil.getSizeRows()$+
' rows and '+
$HMLPSUtil.getSizeCols()$+' columns'" />
getString()
public String getString(int pos, int len)
This method returns the text string beginning at the specified position in the presentation space and continuing for the specified number of characters.
<message title="'Text of row 18:'"
value="'Text:'+$HMLPSUtil.getString(
$HMLPSUtil.getSizeCols()$*17+1,
$HMLPSUtil.getSizeCols()$)$" />
searchString()
public int searchString(int pos, int len)
This method returns the position in the presentation space of the specified string. This method returns 0 if the string is not found in the presentation space.
<varupdate name="$int$" value="$HMLPSUtil.searchString('IBM')$" />
<message title="'Searching for IBM'"
value="'IBM is found at position '+$int$+
' that is row='+
$HMLPSUtil.convertPosToRow($int$)$+
', column='+
$HMLPSUtil.convertPosToCol($int$)$" />
$HMLSessionUtil$
The methods invoked with $HMLSessionUtil$ return values associated with the session. Table 22 summarizes these methods:
| METHOD SUMMARY: $HMLSessionUtil$ | |
|---|---|
| String |
|
| String |
|
| String |
|
Method details
getHost()
public String getHost()
This method returns the host name or the host address that you typed into the Destination Address field of the Connection section of the session configuration (such as myhost.myloc.mycompany.com or 9.27.63.45).
<message title="'Host name or address'" value="$HMLSessionUtil.getHost()$" />
getLabel()
public String getLabel()
This method returns the session name that you typed into the Session Name field of the Connection section of the session configuration (a name such as 3270 Display or 5250 Display).
<message title="'Session name'" value="$HMLSessionUtil.getLabel()$" />
getName()
public String getName()
This method returns the identifying name that the host assigns to the session (such as A , B, or C). When you start a session, the host assigns a name to the session to distinguish it from other instances of the same session that might be started.
<message title="'Session instance identifier'" value="$HMLSessionUtil.getName()$" />
$HMLSQLUtil$
The methods invoked on $HMLSQLUtil$ return information about the results of the most recent SQLQuery action. Table 23 summarizes these methods:
| METHOD SUMMARY: $HMLSessionUtil$ | |
|---|---|
| int |
|
| String |
|
| String |
|
| int |
|
Format of the stored data
The results of the SQLQuery action are stored as a two-dimensional array that is one column wider and one row taller than the size of the block of data returned. Row 0 is used to store the names of the columns (the field names from the database), and Column 0 is used to store a zero-based index (see Table 24 below). The entry at Row 0, Column 0 contains an empty string. The remainder of the array contains the actual data. All values are strings.
Table 24 shows as an example the results of a query, a 3 x 5 block of data, stored in a 4 x 6 array:
| (empty string) | TOPICID | EXMPLID | DESCRIPT |
| 0 | 4 | 18 | Create a toolbar with custom buttons. |
| 1 | 9 | 54 | Attach tables at startup. |
| 2 | 11 | 74 | Edit Products. |
| 3 | 11 | 75 | Enter or Edit Products |
| 4 | 11 | 76 | Find Customers |
In the table above, the entry at Row 0, Column 0 contains an empty string. The remainder of Row 0 contains the field names from the database (TOPICID, EXMPLID, DESCRIPT). The remainder of Column 0 contains index numbers for the rows (0, 1, 2, 3, 4). The actual data is contained in the remainder of the array. All values are strings.
Method details
getColumnSize()
public int getColumnSize()
This method returns the actual number of columns of data in the array, including the added Column 0. For example, for the array in Table 24 this method returns 4.
<message title="'Column size'" value="$HMLSessionUtil.getColumnSize()$" />
getDataByIndex()
public int getDataByIndex(int row, int column)
This method returns the entry at the specified row and column index. The following list shows the values returned for the data shown in Table 24:
- getDataByIndex(0,0) returns an empty string.
- getDataByIndex(0,1) returns the string 'TOPICID'.
- getDataByIndex(0,2) returns the string 'EXMPLID'.
- getDataByIndex(1,1) returns the string '4'.
- getDataByIndex(2,2) returns the string '54'.
- getDataByIndex(3,3) returns the string 'Edit Products'.
<message title="'Row 3, Column 3'"
value="$HMLSessionUtil.getDataByIndex(3,3)$" />
getDataByName()
public int getDataByName(int row, String fieldName)
This method returns the entry at the specified row and field name. The following list shows the values returned for the data shown in Table 24:
- getDataByIndex(1, TOPICID) returns the string '4'.
- getDataByIndex(2, EXMPLID) returns the string '54'.
- getDataByIndex(3, DESCRIPT) returns the string 'Edit Products'.
<message title="'Row 3, Field DESCRIPT'"
value="$HMLSessionUtil.getDataByName(3,'DESCRIPT')$" />
getRowSize()
public int getRowSize()
This method returns the actual number of rows of data in the array, including the added Row 0. For example, for the array in Table 24 this method returns 6.
<message title="'Column size'" value="$HMLSessionUtil.getRowSize()$" />
FormatNumberToString() and FormatStringToNumber()
$FormatNumberToString()$ is deprecated in favor of $HMLFormatUtil.numberToString()$. The former has the same input parameters and return type as the latter (see numberToString()).
$FormatStringToNumber()$ is deprecated in favor of $HMLFormatUtil.stringToNumber()$. The former has the same input parameters and return type as the latter (see stringToNumber()).