Horizontal scaling topology
Horizontal scaling exists when there are members of an application server cluster on multiple physical machines. Having cluster members on several machines lets a single application span the machines, yet still present a single system image.
The following figure shows an example of horizontal scaling.
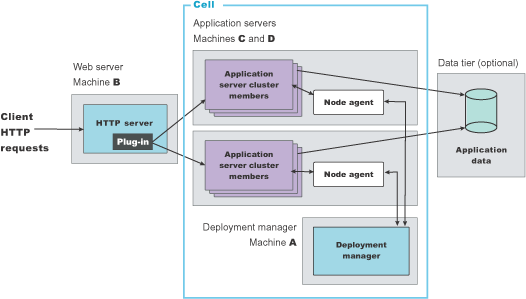
In this example, the Web server on Machine B distributes requests to clustered Application Servers on Machines C and D. Cluster members on Machines C and D are created in the same cluster.
You can combine a load balancer to distribute client HTTP requests with clustering, to reap the benefits of both types of horizontal scaling. The Load Balancer topology topic describes this system configuration.
Typical use
Horizontal scaling provides the increased throughput of vertical scaling topologies but also provides failover support. This topology lets you handle Application Server process failure and hardware failure without significant interruption to client service. You can also use horizontal scaling to optimize the distribution of client requests through mechanisms, such as workload management or remote HTTP transport.

Setting up a multinode environment