Vertical scaling topology
Vertical scaling refers to setting up multiple application servers on one machine, usually by creating cluster members.
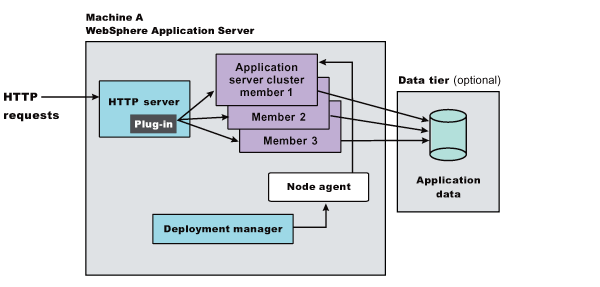
This topology illustrates a simple vertical scaling example, with multiple cluster members of an Application Server on Machine A. You can also implement vertical scaling on more than one machine in a configuration. Combine vertical scaling with other topologies to boost performance and throughput.
Typical use
Vertical scaling offers the following advantages:
- Increased processing power efficiency. An instance of an application
server runs in a single Java virtual machine (JVM) process. However, the inherent
concurrency limitations of a JVM process prevent it from fully utilizing the
processing power of a machine. Creating additional JVM processes provides
multiple thread pools, each corresponding to the JVM process associated with
each Application Server process. This correspondence avoids concurrency limitations
and lets the Application Server use the full processing power of the machine.
- Load balancing. Vertical scaling topologies can use the WebSphere
Application Server workload management facility.
- Process failover. A vertical scaling topology also provides failover support among Application Server cluster members. If one Application Server instance goes offline, the other instances on the machine continue to process client requests.
Single machine vertical scaling topologies have the drawback of introducing the host machine as a single point of failure in the system. Vertical scaling on multiple machines avoids the single point of failure.
Instructions
To set up a vertical scaling topology, use the administrative console to configure a set of Application Server cluster members that reside on the same machine.
It is recommended that you plan vertical scaling configurations ahead of time. However, because vertical scaling does not require any special installation steps, you can implement vertical scaling whenever it is needed.
While you are deciding how many cluster members to create on a machine, take these factors into account:
- The design of the application. Applications that use more components
require more memory, limiting the number of cluster members you can run on
a machine.
- The hardware environment. Vertical scaling works best with plenty of memory and processing power. Eventually there is a point of diminishing returns on any machine, where the overhead of running more cluster members cancels out the benefits of adding them.
The best way to ensure good performance in a vertical scaling configuration is to tune a single instance of an Application Server for throughput and performance, then incrementally add cluster members. Test performance and throughput as you add each cluster member. Always monitor memory use when you are configuring a vertical scaling topology, so you do not exceed available physical memory on the machine.

Setting up a multinode environment