Performance reports
Overall
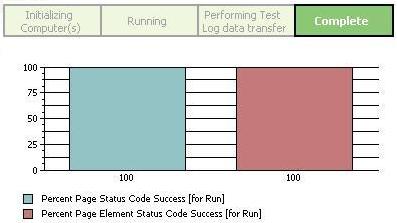
The Overall page provides...
- Progress indicator showing state of the run.
- Bar chart showing...
- Percentage of page success HTTP status codes
- Percentage of page element success HTTP status codes.
- If set, the percentage of success page title verification points.
Successful HTTP status codes are those in the 200 or 300 category. Unexpected responses are in the 400 or 500 category.
Summary

The Summary page includes
- Run Summary
- Name of the test.
- Number of active and completed users.
- Elapsed time.
- Status of the run.
Status can be...
- Initializing Computers
- Adding Users
- Running
- Transferring data to test log
- Stopped
- Complete
By default, results are displayed for all hosts. For individual computers, click the computer name in the Performance Test Runs view.
- Page Summary...
- Total number of page attempts and hits.
Attempts do not not include requests within the page. Hits means the server received the primary request and returned a complete response.
- Average response time for all pages.
Sum of response times for all page elements (including connect time and inter-request delays). Does not include response times for pages containing requests with status codes...
- 4XX (client errors)
- 5XX (server errors)
The only exception is when the failure (for example, a 404) is recorded and returned, and the request is not the primary request for the page. Page response times which contain requests that time out are always discarded.
- The standard deviation of the average response time for all pages.
- Maximum response time for all pages.
- Minimum response time for all pages.
- A summary of the results for page verification points, if these verification points were set.
- Total number of page attempts and hits.
- Page Element Summary information...
- Total number of page element attempts and hits.
A page element attempt means that a request was sent. A hit means that the server received the request and returned any complete response.
- Total number of page elements where no request was sent to the server because the client determined that the page elements were fresh in the local cache.
- Average response time for all page elements.
Time between the first request character sent and the last response character received. Response times for HTTP requests that time out or that return an unexpected status code (the recorded and played back codes do not match) in the range of 4XX (client errors) to 5XX (server errors) are discarded from the reported values.
- The standard deviation of the average response time.
- The percentage of verification points that passed.
- A summary of the results for page element verification points, if these verification points were set.
If you have set transactions in the test, the Summary page displays the following Transaction information:
- Minimum, maximum, and average response time for all transactions. Response time is the actual time spent within the transaction container.
- The standard deviation of the average response time.
- Total number of transactions that were started and the total number that have been completed.
- Total number of page element attempts and hits.
Page Performance
The Page Performance page shows the average response of the slowest 10 pages in the test as the test progresses. With this information, you can evaluate system response during and after the test.
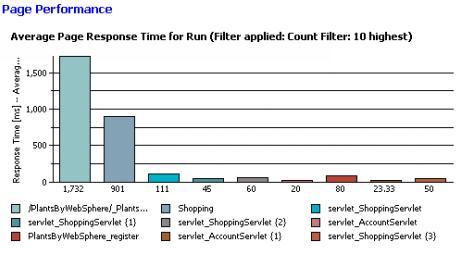
The bar chart shows the average response time of the 10 slowest pages. Each bar represents a page that you visited during recording. As you run the test, the bar chart changes, because the 10 slowest pages are updated dynamically during the run. For example, the Logon page might be one of the 10 slowest pages at the start of the run, but then, as the test progresses, the Shopping Cart page might replace it as one of the 10 slowest. After the run, the page shows the 10 slowest pages for the entire run.
The table under the bar chart provides the following additional information:
- Minimum response time for each page in the run.
Response time is the time between the first request character sent and the last response character received. Response time counters omit page response times for pages containing requests with status codes in the range of 4XX (client errors) to 5XX (server errors). The only exception is when the failure (for example, a 404) is recorded and returned, and the request is not the primary request for the page. Page response times which contain requests that time out are always discarded.
- Average response time for each page in the run. This matches the information in the bar chart.
- Maximum response time for each page in the run.
- The number of attempts per second to access each page.
An attempt means that a primary request was sent; it does not include requests within the page.
- Total number of attempts to access the page.
To display the 10 slowest page element response times, right-click a page and click Display Page Element Responses.
Response vs. Time Summary
The Response vs. Time Summary page shows the average response trend as graphed for a specified interval. It contains two line graphs with corresponding summary tables. When a schedule includes staged loads, colored time-range markers at the top of the graph delineate the stages.
- The Page Response vs. Time graph shows the average response time for all pages during the run.
Each point on the graph is an average of what has occurred during that interval. The table after the graph lists the total average response time for all pages in the run and the standard deviation of the average response time.
- Page Element response vs. Time
Shows the average response time for all page elements during the run.
Each point on the graph is an average of what has occurred during that interval. The table under the graph lists the total average response time for all page elements in the run and the standard deviation of the average response time. The table also lists the total number of page elements where no request was sent to the server because the client determined that the page elements were fresh in the local cache. You set the Statistics sample interval value in the schedule, as a schedule property.

Response vs. Time Detail
The Response vs. Time Detail page shows the response trend as graphed for the sample intervals. Each page is represented by a separate line.
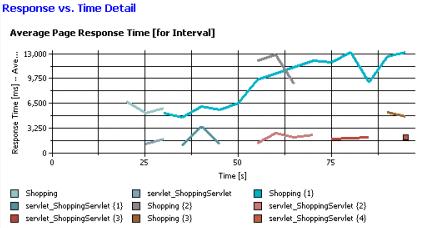
The Average Page Response Time graph shows the average response of each page for each sample interval.
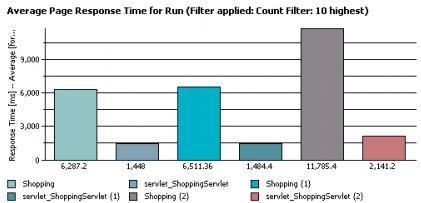
When a schedule includes staged loads, colored time-range markers at the top of the graph delineate the stages. The table after the graph provides the following additional information:
- Minimum page response time for the run. Response time is the time between the first request character sent of the primary request and the last response character received. Response time counters omit page response times for pages containing requests with status codes in the range of 4XX (client errors) to 5XX (server errors). The only exception is when the failure (for example, a 404) is recorded and returned, and the request is not the primary request for the page. Responses that time out are discarded.
- Average page response time for the run. This is similar to the graph, but the information in the table includes the entire run.
- Maximum page response time for the run.
- Standard deviation of the average response time.
- Rate of page attempts per interval for the most recent statistics sample interval.
A page attempt means that the primary request was sent; it does not include requests within the page. You set the Statistics sample interval value in the schedule, as a schedule property.
- Number of page attempts per interval.
Page Throughput
Frequency of requests being transferred per sample interval...
- Page Hit Rate
Page attempt rate and page hit rate per sample interval for all pages.
A page attempt means that the primary request was sent; it does not include requests within the page.
A hit means that the server received the primary request and returned any complete response.
When a schedule includes staged loads, colored time-range markers at the top of the graph delineate the stages. The summary table after the graph lists the total hit rates and counts for each page in the run.
- User Load
Active users and users that have completed testing, over the course of a run.
The summary table after the graph lists the results for the most recent sample interval. You set the Statistics sample interval value in the schedule, as a schedule property. As the run nears completion, the number of active users decreases and the number of completed users increases. The summary table after the graph lists the active and completed users for the entire run.
To set the sample interval value, open the schedule, click the Statistics tab, and then view or modify Statistics sample interval.
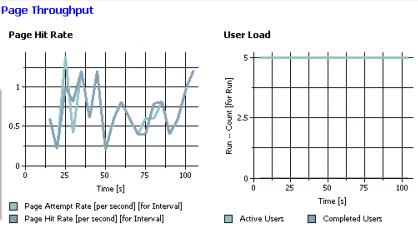
If the number of requests and hits are not close, the server might be having trouble keeping up with the workload.
If you add virtual users during a run and watch these two graphs in tandem, you can monitor the ability of the system to keep up with the workload. As the page hit rate stabilizes, even though the active user count continues to climb and the system is well tuned, the average response time will naturally slow down. This response time reduction happens because the system is running at its maximum effective throughput level and is effectively throttling the rate of page hits by slowing down how quickly it responds to requests.
Server Throughput
The Server Throughput page lists the rate and number of bytes that are transferred per interval and for the entire run. The page also lists the status of the virtual users for each interval and for the entire run.
- Byte Transfer Rates graph
Rate of bytes sent and received per interval for all intervals in the run.
When a schedule includes staged loads, colored time-range markers at the top of the graph delineate the stages. The summary table after the graph lists the total number of bytes sent and received for the entire run.
- User Load
Active users and users that have completed testing, per sample interval, over the course of a run.
You set the Statistics sample interval value in the schedule, as a schedule property. As the run nears completion, the number of active users decreases and the number of completed users increases. The summary table after the graph lists the active and completed users for the entire run.
The bytes sent and bytes received throughput rate, which is computed from the client perspective, shows how much data Rational Performance Tester is pushing through your server. Typically, you analyze this data with other metrics, such as the page throughput and resource monitoring data, to understand how network throughput demand affects server performance.
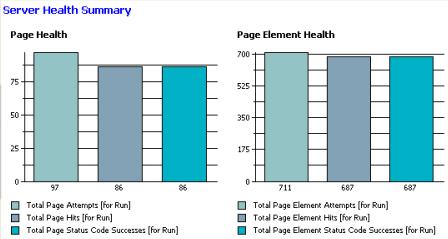
Server Health Summary
The Server Health Summary page gives an overall indication of how well the server is responding to the load.
- Page Health
The total number of page attempts, page hits, and status code successes for the run.
The table under the bar chart lists the same information.
A page attempt means that a primary request was sent; it does not include requests within the page.
A hit means that the server received the primary and returned any complete response.
A success means that the response code verification point passed for that request. If the request has no verification points, a success means that the server received a request and returned a response where the status code was in the 200 or 300 category or returned an expected response in the 400 or 500 category.
- Page Element Health
Total number of page element attempts, page element hits, status code successes, and page element redirections for the run.
The table under the bar chart lists the same information and the total number of page elements where no request was sent to the server because the client determined that the page elements were fresh in the local cache.
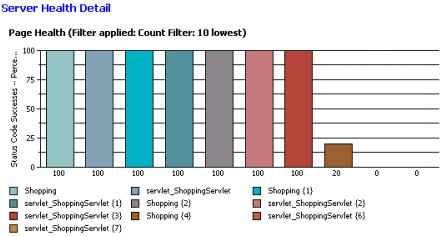
Server Health Detail
The Server Health Detail page provides specific details for the 10 pages with the lowest success rate.
- The bar chart shows the 10 pages with the lowest success rate.
- The summary table under the chart lists, for all pages, the number of attempts, hits, and successes in the run and the attempts per second during the run.
An attempt means that a primary request was sent; it does not include requests within the page.
A hit means that the server received the primary and returned any complete response.
A success means that the response code verification point passed for that request. If the request has no verification point, a success means that the server received a request and returned a response where the status code was in the 200 or 300 category or returned an expected response in the 400 or 500 category.
Caching Details
The Caching Details page provides specific details on caching behavior during a test run.
- The Caching Activity graph shows the total number of page element cache attempts, page element cache hits, and page element cache misses for the run.
These values correspond to responses from the server, indicating whether the content has been modified. Additionally, the bar chart shows the total number of page elements in cache that were skipped for the run. That value indicates the cache hits that were still fresh in the local cache, where communication with the server was not necessary.
- The Page Element Cache Hit Ratios graph shows the percentage of cache attempts that indicate server-confirmed success and client-confirmed success for the run.
Server-confirmed cache hits occur when the server returns a 304 response code. Client-confirmed cache hits occur when the content is still fresh in the local cache and no communication with the server is required.
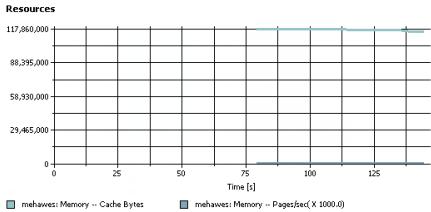
Resources
The Resources page shows all resource counters that were monitored during the schedule run.
- The Resources graph shows the values of the resources that counters monitored during the schedule run. When a schedule includes staged loads, colored time-range markers at the top of the graph delineate the stages.
The chart scales automatically to accommodate the highest resource counter value.
- The summary table under the chart lists the most recent values of the resource counters that were monitored during the schedule run. This table also lists the minimum, maximum, and average values of the resource counters that were monitored during the schedule run. This table is organized by resource monitoring hosts.
Page Element Responses
The Page Element page shows the 10 slowest page element responses for the selected page.
Page Response Time Contributions
The Page Response Time Contributions page shows how much time each page element contributes to the overall page response time and the client delay time and connection time.
Standard deviation
How tightly data is grouped about a mean.
For example, hosts foo and bar both have an average response time of 12 seconds. Host foo has response times of 11, 12, 13, and 12 ms. Host bar has response times of 1, 20, 25, and 2. Although mean time is the same, the standard deviation of host bar is greater.
Related concepts:
Why response time of a page does not equal the sum of its requests
Related reference:
Page Element report
Page Percentile report
Verification Points report
Error 404 - Not Found
The document you are looking for may have been removed or re-named. Please contact the web site owner for further assistance.