Roles
A role combines a set of allowed actions with specific resources. The set of allowed actions is called a role type.
For example, the role type Editor contains allowed actions like...
- view resources
- modify resources
- create new resources
Roles are denoted as...
-
RoleType@Resource
For example, the Editor role type combined with the Market News Page resource results in the role...
-
Editor@Market News Page
By default, this role would also allow editor-style access on descendant resources underneath the Market News Page through inheritance.
Role types contain all allowed actions contained in the role types them in the hierarchy. For example, Privileged Users and Editors can do everything that Users can do. Managers can do everything that editors and Users can do.
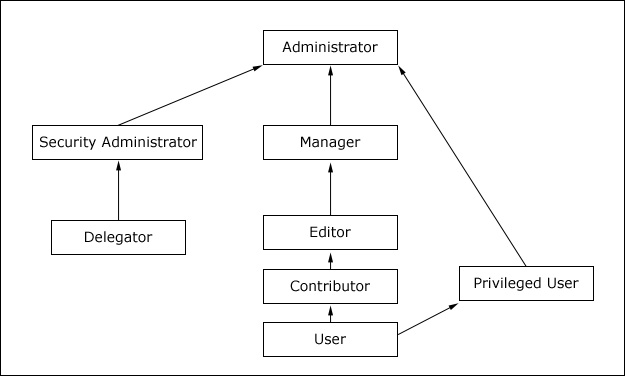
Role types
| Role Type | Allowed Actions |
|---|---|
| Administrator | Unrestricted access on resources.
This includes creating, configuring, and deleting resources. Administrators can also change the access control settings on resource; in other words grant other people access to those resources. |
| Security Administrator | The user with this role type can delegate a subset of their privileges on a resource to other people according to the Delegated Administration Policy.
For example, a user who is assigned roles...
...on a resource can assign the editor role to other people provided he has delegator role on those people. Having the Security Administrator role on a resource alone does not give view or edit access to the resource. |
| Delegator | Allow user to grant roles.
The set of roles that can be granted is defined through the roles types...
For example a user has a Delegator role on the SalesTeam user group but no Delegator role on the Managers user group, so this user can grant roles only to the SalesTeam or individual members of the SalesTeam user group but not to the Managers user group. Having the Delegator role on a resource does not give direct access to the resource. The purpose of the Delegator role type is to allow the granting of roles to users or groups, so assigning Delegator role on resources or resource types that are not users or user groups will not grant those users additional privileges. |
| Manager | Create new resources and configure existing resources used by multiple users. |
| Editor | Create new resources and configure existing resources used by multiple users. |
| Contributor | View portal content and create new resources.
The Contributor role type does not include the permission to edit resources. It only allows you to create new resources. For example, a user is granted the Contributor role on the template category Teamspaces. The user will not be able to modify the category itself but can create new templates in this category. Available for the following resources:
|
| Privileged user | View portal content, customize portlets and pages, and create new private pages. |
| User | View portal content. |
| No role assigned | Cannot interact with resource. |
Inheritance
Each resource in the hierarchy inherits the role assignments of its parent resource. When you assign a group to a role on a parent resource, the group automatically acquires that same set of allowed actions for all child resources.
Inheritance can be blocked...
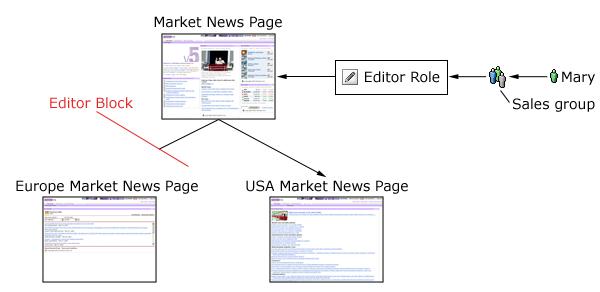
Application Roles
Application roles can contain an arbitrary set of other roles. For example...
- Editor@Market News page
- Editor@Market News portlet
This makes it possible to use application roles to bundle cohesive allowed actions, simplifying access control administration. Application roles with the same name in different database domains are correlated so it is possible to aggregate roles from different database domains within one application role.
Access control portlets are not set up to handle application roles, but application roles can be handled through the XML configuration interface.
Role Assignments
Roles are assigned to users and groups that are contained in the user registry. Roles can be assigned by someone with the necessary authorization, such as the portal administrator, in any of three ways:- Explicitly assigned to an individual user
- Implicitly assigned through group membership. If a group has a role, all members of the group automatically acquire the role. Nested groups (groups that are members of another group) inherit role assignments from their parent groups.
- Inherited through a role assignment on a parent resource. By default roles on a resource automatically apply to all children of that resource unless role blocks are used.
Users and groups can have multiple roles on the same resource. For example, a user might have both the Editor and Manager roles on a particular page. One of these roles might be inherited through the resource hierarchy and the other might be explicitly assigned.
Assign roles to individual users only in exceptional cases. Assigning roles to user groups and managing effective user privileges by adding to or removing users from those groups reduces the number of role mappings and simplifies maintenance.
Ownership
Each resource can have a dedicated owner. The resource owner can be a single user or a single user group. When a user creates a new resource, such as a page, the user automatically becomes the initial owner of that resource.
For non-private resources, which are resources accessible by those people having been granted access to the resource, ownership provides the same set of allowed actions as the Manager role type. For private resources, which are resources accessible only by the owner of the resource ownership provides the same set of allowed actions as the Privileged User role type plus the allowance to delete the resource. So in the case of both non-private and private resources, these allowed actions include the ability to delete the resource.Private resources can only be owned by users, not by user groups. It is not possible to define roles on private resources, and resource ownership cannot be inherited.
Use the XML configuration interface or the Resource Permissions portlet to change the owner of a resource.
Private pages
A private page can be accessed only by its owner. Privileged Users (users assigned a role of type Privileged User) can explicitly create new private pages that are accessible only by themselves. Additionally, a Privileged User on a non-private page can personalize the page and create new private pages underneath it. Customizing a non-private page usually creates a private copy of the corresponding non-private page. Any changes that a Privileged User makes to a non-private page are not accessible by other users.
Private pages cannot be controlled by an external security manager. Access control for private pages is always internally controlled by WebSphere Portal.
Traversal support
Users with role assignments on resources of type Page or URL Mapping do get the implicit permission to navigate to those resources. These users are guaranteed the ability to navigate through all parent resources of those resources. Users only see the title of those resources, while the corresponding resource content (for example the portlets on the page) remains inaccessible unless those users have further role assignments granting them normal access to those resources.
Parent topic
Resources, roles, and policies
Related reference
Delegated Access Control Administration