Overview
| Industry architectures | |||
| Retail & CPG | Supply chain | Automotive | Insurance |
| Security and compliance | |
| Security | Multicloud identity and management |
| Advanced technology | |||
| Analytics & AI | Blockchain | Mobile | IoT |
| Enabling architectures | |||||
| Digital business automation | Data | Cloud-native | Application modernization | Event-driven | Integration |
| Multicloud platform architectures | |||||
| Public cloud | Private cloud | Virtualization | Edge | Power | Z |
| Open cloud platform |
| Built on Red Hat technology |
| Management and operations | |||
| Service management | Multicloud management | DevOps | Resilience |
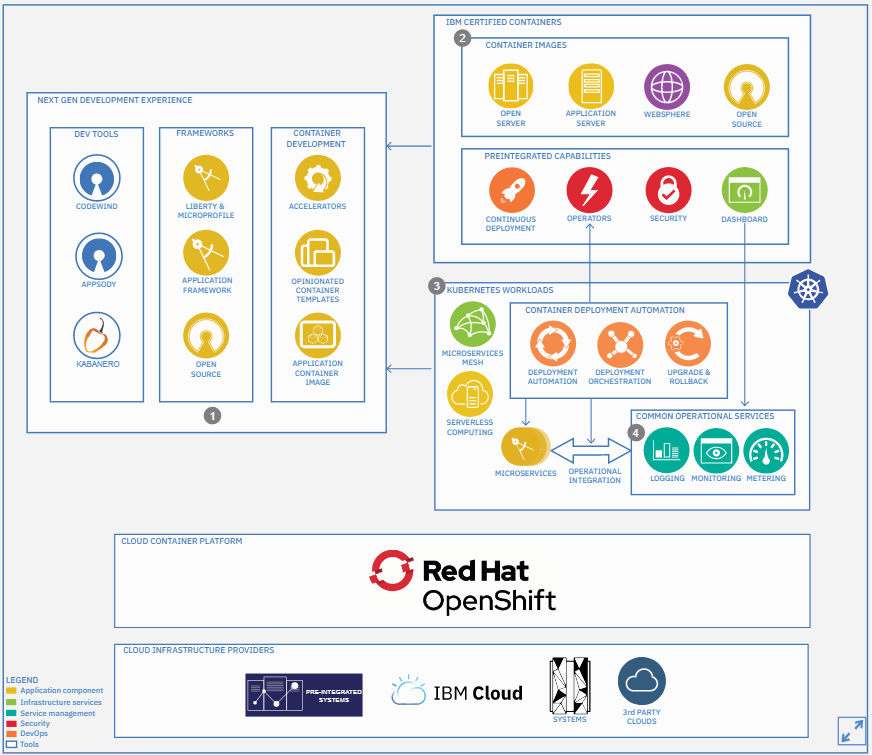
Cloud Native Architecture
The Cloud-native application reference architecture includes public, private, and hybrid clouds. Techniques containers, service meshes, and microservices.
Nonfunctional requirements
Security
Security architecture includes...
- TLS/SSL certificate management
- microservice-based network security policies
- distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) protection
- web application firewalls (WAF)
Authentication can be provided by a service mesh, such as Istio:
- Provide each service with an identity for interoperability across clusters and clouds
- Secure service-to-service communication and user-to-service communication
- Provide a key management system to automate key and certificate generation, distribution, rotation, and revocation
Service management
Service management architecture includes:
- Health checks
A health-check API endpoint to a microservice validates the status of a component and all its dependencies. If a service's liveness probe fails, Kubernetes removes the application instance and starts a new one to replace it. Readiness probes are used to determine whether the container is ready to handle requests. Kubernetes doesn't route work to a container that has a failing readiness probe.
- Logging
Logs provide visibility into the behavior of a running application component and microservice.
- Metrics
Understand the performance of individual systems or the overall performance aggregated across general dimensions.
- Distributed tracing
A unique transaction ID is passed through the call chain of each transaction. Latency analysis attaches timing information to the transaction. Correlate the captured transaction ID with application and service identification and other metadata. We can configure Istio-enabled applications to collect trace spans by using Zipkin or Jaeger.